-
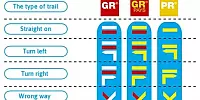
GR, GRP, PR: What do the French hiking signs mean?
What are the coloured symbols on French hiking routes? Who paints them there and why?
-
Miss France: glam - but not sexy
Miss France organiser Geneviève de Fontenay fears she is fighting a losing battle to protect her 'Cinderella dream' from vulgarity
-
Normandy Landings visit for Queen
Queen Elizabeth has confirmed a state visit to France, ending rumours she is handing over duties to Charles
Megaliths and mega-myths
Carnac, King Arthur and Brittany's sights of the Round Table
Not for nothing is the region of Brittany known as the Land of Legends: its Celtic druidic heritage, medieval Arthurian tales and folklore of spirits and goblins make for a heady witch's brew. The landscape, too, plays a role: the moors and forests, standing stones and rugged coasts fire the imagination.
Megalithic sites such as Carnac have long been linked with the Celtic druidic cults, though their builders are now known to date from the earlier Neolithic period (around 5200-2200BC).
However, the first settlements in Brittany date from much earlier. Traces of fires and stone cutting have been found in areas in Morbihan and Finistère that were later covered by the sea when the Ice Age glaciers melted 10,000 years ago.
That perhaps gave rise to the legend of Ys (the subject of Edouard Lalò's opera Le Roi d'Ys). Ys was a fine town built by King Gradlon of Cornouaille for his pleasure-loving daughter Dahud in what is now the Bay of Douarnenez.
It was protected from the sea by a dyke, to which the king kept the key around his neck. Dahud met a charming knight, who persuaded her to steal the key as the king slept. She gave it the knight, who was none other than the Devil, and he opened the dyke and flooded the town.
The Celts arrived from central Europe in the middle of the first millennium BC and are the people most associated with Breton culture: each August, the Festival Interceltique de Lorient sees approaching a million visitors celebrate the music and culture of the "Celtic" lands Brittany, Ireland, Scotland, Cornwall and Wales, all of which retain languages from the period.
A druid revival dating to the 19th century also flourishes in Wales, Cornwall and Brittany.
The Gauls were Celts, with their gods and goddesses such as light god Belenos, thunder god Taranis or protector of the tribe Toutatis, familiar to readers of Asterix.
Strictly speaking, the first Bretons were Celtic refugees from Britain who fled Anglo-Saxon invaders. The area was called la Petite Bretagne (Little Brittany) from the British mainland, la Grande Bretagne.
Legend says King Arthur was a Briton who fought the Anglo-Saxons, ruled both Brittanies and will one day return to reunite them. Brittany is also said to be the home of tragic lovers Tristan and Iseut (Isolde), with some accounts making
Tristan one of Arthur's knights.
Brocéliande, King Arthur and Excalibur
KING Arthur and his knights had many adventures in the Forest of Brocéliande, said to be today's Forest of Paimpont, and their exploits in the Dark Ages were sung by bards, then Welsh historian Geoffrey of Monmouth drew the tales together in History of the Kings of Britain in 1135.
He said Arthur was king of lands in France as well as Great Britain. Chrétien de Troyes, also in the 12th century, was among French writers who spread his fame.
The tourist office adviser in Tréhorenteuc, in the Forest of Paimpont, said: "The legend was born in Great Britain, around the 5th century, but it spread by word of mouth, notably because of the flight of the Celts to la Petite Bretagne. The best-known story is the meeting between Merlin and Viviane, the Lady of the Lake."
Some say the fairy Viviane gave Arthur his sword, Excalibur; other tales tell of how she guided the dying king to the magical Isle of Avalon; how she educated Lancelot after his father's death; or of the fateful consequences of the meeting with Merlin: she persuaded him to teach her magic in return for her love, but turned her new skills on him.
"Merlin and Viviane met in the Fountain of Barenton [west of the forest near a site called Folle Pensée: mad thought] and, out of love, he let himself be trapped in an invisible prison and can never leave. Legend says he is still
there, although there is a megalithic site called Merlin's Tomb, in homage to him."
Another story has it he, too, was born in the forest, and Breton folklorist DamEnora said: "His father was a demon and he was born ugly and covered with hair like an animal and only afterwards lost his hair."
One megalithic site is called l'Hotie de Viviane (Viviane's House), while people claim to have seen the underwater crystal palace Merlin built for Viviane at the Château de Comper's lake. The chateau houses the Centre de l'Imaginaire Arthurien legend site.
Merlin also taught magic to Morgan le Fay, Arthur's half-sister. Betrayed by a lover, she used to imprison unfaithful knights who passed through the forest in the Val sans Retour (Valley of No Return).
Only Lancelot, because of his faithful love for Queen Guinevere, could escape and break the enchantments that held them prisoner. At Le Pont du Secret (Bridge of the Secret), Guinevere admitted she loved him too, DamEnora said.
"There are many valleys where the countryside creates a feeling of mystery," the tourist office adviser said. "People who walk in the forest say the scenery itself makes you dream."
A more recent tourist sight is L'Or de Brocéliande, a tree covered in gold leaf that commemorates a forest fire. "It represents the precious nature of the forest," she said.
Celtic druids are remembered in Christian rites
THE Celtic priesthood of druids are long gone: mainly known from Roman authors and archaeological finds, they have inspired several contemporary groups, of which the best-known French one is the Breton Gorsedd, founded in the 18th
century. It is affiliated to the Welsh group that runs the national Eisteddfod.
With no explicit pagan beliefs, Breton druids say theirs is a philosophy of life compatible with various faiths, or none. They meet for ceremonies on occasions such as the solstices, equinoxes and the Celtic festivals of Samhain,
Beltane and Imbolc. There is also a celebration of Breton culture in July, the Gorsedd Digor, which the public can attend.
Ancient druids worshipped a Celtic pantheon and believed in an afterlife called le Monde Blanche (the White World), from which one would be reincarnated. Julius Caesar said their rites included human sacrifice.
Current Breton Grand Druide Per Vari Kerloc'h said the stories may be true, but those killed were thought to have been criminals.
"The person who abolished human sacrifice in Gaul was [politician] Robert Badinter [in 1981]. In the last years, the executions were discreet, but until end of the 19th century were held in public," he said.
The druids are thought to have worshipped in forest groves and in wooden temples similar to Greek or Roman ones, Mr Kerloc'h said.
"There have been excavations at Gaulish temples in the north and in Belgium, which were linked to a warrior cult. War trophies were found and, we think bodies of enemies were placed in them to rot, and their bones kept, like in an
ossuary."
The mountain Mané Guen at Guénin, Morbihan, is especially associated with the druids. Mr Kerloc'h said: "It was one of the sacred places of the Venates, the Gaulish tribe that lived there, and people imagine there were sacrifices there. A chapel was built there to Christianise a Celtic holy place.
"Locronan, Finistère, was linked with them and is a place of Christian pilgrimage, which replaced a druidic cult based on the Celtic calendar. The stopping places on the Troménie pilgrimage are linked to annual cycles. We reestablished
our own version, which we do before the Catholic one, with our own rituals."
Mr Kerloc'h said his group did not claim to reconstruct Celtic practices. "Our relationship with the ancients is a symbolic one. Our rituals take place in nature, in the open air, in connection with the cycles of nature and of the cosmos. Man is part of nature and that is why we pay homage to it and believe that we must preserve it to preserve ourselves. It is a question of survival and respect of that which sustains our lives."
He said the Romans started to suppress the druids, but the worship of Celtic gods continued, integrated alongside the Roman ones. The process was finished after Christianisation, when Catholicism became the official religion, he said.
"They used the secular power of Rome to forbid other beliefs. At least that is the official story, but you can't get rid of a whole way of thinking just like that. We think the druidic traditions continued and some were Christianised, such as All Saints' Day and the Day of the Dead (November 1 and 2), which is based on the Celtic Samhain.
"Saint Brigid's Day in February is a festival of lights that is an adaptation of the worship of fire goddess Brigid, whose cult was especially popular at Kildare in Ireland. So some things were perpetuated in a new form. We see it particularly in the cult of the saints: in Catholic dogma, there is only one god, but many practices treat them like little gods.
"We believe druidic traditions have been passed down in folk practices and legends, more or less Christianised. They are enough to legitimise groups such as ours, based on folk traditions, not fantasies."
Menhirs, burial mounds and the fertility cults
PREHISTORIC sites are dotted all over Brittany, including upright single stones (menhirs), structures with a long stone on top of two upright ones (dolmens), alignments, tumuli (burial mounds) and cairns.
Carnac, in Morbihan, is the best-known megalithic site. It has 3,000 standing stones, dating from around 5000BC to 3000BC. Its alignments may have pointed to sacred spaces, although legend says St Cornély turned marching Roman soldiers
into stone as they chased him.
Dolmens and cairns, however, are known to have had burial functions, because bones and offerings have been found inside, said Emmanuelle Vigier, director of the Carnac Prehistory Museum.
"At Carnac, one ancient monument, the Tumulus Saint-Michel, is comparable to the pyramids. It is a hill, an immense construction, with a single tomb. High-value jade items were found inside it.
"When it comes to the single menhirs or alignments, the function is less certain, but we know building and erecting them would have taken a huge workforce and, unlike the earlier nomadic hunter-gatherers, there had to have been a village, a social grouping with a hierarchy.
"They had started to build permanent houses and have agriculture and to raise animals. They made monumental tombs because they were going to stay."
Ms Vigier added: "With so many monuments at Carnac, it must have been an important, rich European centre in the 5th millennium BC. Valuable objects from Italy, Spain and Portugal have been found. It is thought its wealth was based on the salt trade. It was a kind of New York of its time. The whole of Carnac is on granite and most of the megaliths were made from stone from within a few hundred metres. The material was there, ready to use."
Druid Per-Vari Kerloc'h said they have been associated with standing stones since the Romantic period (early 19th century) and they sometimes hold ceremonies at such sites. It is no longer believed the megalithic structures were built for the druids, but they would have used them, because they retained a tradition as a link to the supernatural.
Mr Kerloc'h said: "Through the ages, the megaliths have always been used and associated with certain traditions; they are more than just part of the scenery. They are often associated with cults of fertility. The [phallic] symbolism
of menhirs is fairly obvious, and women used to go and rub their stomachs against them. In Locronan, women used to lie on a megalith to be made fertile by the rising sun."
Watch out for the Little People: they're unfriendly
FOLKLORE is full of the Little People, with fairies, elves and the korrigans. DamEnora (http://damenoraconteusebroceliande.unblog.fr) said: "The korrigans are the best-known.
"Children see them as cute little imps, but they are actually nasty little buggers that are very capricious. People claim to have seen them. They are our rascally side we keep hidden and pretend does not exist."
"They are not pretty, unlike the elves, but even elves are not always friendly; the Little People generally are not, apart from the Parisette, a sweet fairy, about 20cm high who goes around in the nude.
"She protects walkers in the forest from creatures like a monster that lives in the lakes and will grab you by the foot if you go too close. There is also the Pouka, a witch/devil that lives in cemeteries. She will, very nicely, suck out your blood without batting an eyelid."
DamEnora said a character unique to Brittany is the Ankou, Death's servant. "If one night you are sitting at home and you hear a cart going by, don't go out. It's the Ankou who has come for your soul; if you go out, he'll put you on your cart.
"He's a thin, bony character with a big black cloak and a big felt hat shading his empty eyes. He points his crooked finger at you and calls, and you have to obey."
Sometimes, she added, he hides in empty houses and waits for a passer-by. "If you see a glimmer of light. even though there is no on there, and the door is ajar, don't go in.
"Old people, and some young people, still believe in him. Old people will not go out if they hear an owl cry, because it represents death.
"People would nail a dead owl to the door of their house to scare death and bad luck away. On certain nights if you knock at a door, people will not answer, not to be unfriendly, but because they are afraid."